Types of Hearing Aids
Addressing hearing loss requires a comprehensive and professional approach. This guide outlines the various hearing aid types available in Pakistan and emphasizes the critical role of professional fitting in achieving optimal hearing outcomes.

Types of Hearing Aids: A Comprehensive Guide
Hearing aids are sophisticated devices designed to amplify sound and improve communication for individuals with hearing loss. With advancements in technology, modern hearing aids come in various styles, each offering unique features and benefits. The right choice depends on factors such as the type and severity of hearing loss, lifestyle preferences, and personal comfort.
This guide provides an in-depth look at the different types of hearing aids, their advantages, disadvantages, and suitability for various users.
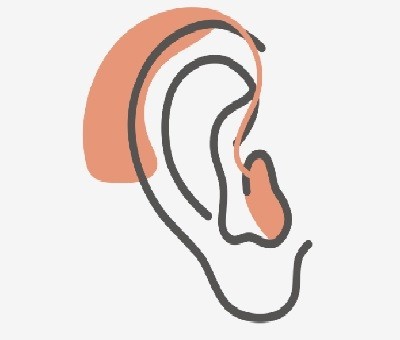
1. Behind-the-Ear (BTE) Hearing Aids
Description:
BTE hearing aids have a durable plastic casing that sits behind the ear. A clear tube connects the case to an earmold or dome that fits inside the ear canal.
Advantages:
-
Suitable for mild to profound hearing loss.
-
Durable and reliable, with a longer lifespan than smaller styles.
-
Accommodates advanced features such as telecoil, Bluetooth connectivity, and directional microphones.
-
Generally has a longer battery life due to larger battery size.
Disadvantages:
-
More visible than smaller styles, which may be a concern for some users.
-
Can be less comfortable for those who wear glasses.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals of all ages, including children.
-
Those with mild to profound hearing loss.
-
People who prioritize durability and extended battery life.
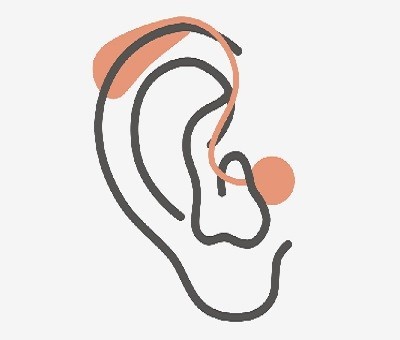
2. Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) / Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE) Hearing Aids
Description:
RIC/RITE hearing aids resemble BTE models but with a key difference: the receiver (speaker) is positioned in the ear canal, connected by a thin wire to the behind-the-ear component.
Advantages:
-
More discreet than traditional BTE hearing aids.
-
Provides superior sound quality due to the placement of the receiver.
-
Lightweight and comfortable to wear for extended periods.
Disadvantages:
-
The receiver is exposed to earwax and moisture, which can affect durability.
-
Smaller size may make handling and maintenance more challenging.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with mild to severe hearing loss.
-
Those looking for a balance between aesthetics, comfort, and functionality.
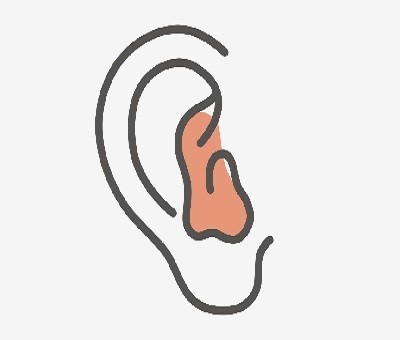
3. In-the-Ear (ITE) Hearing Aids
Description:
ITE hearing aids are custom-molded to fit within the outer ear. They house all components in a single shell.
Advantages:
-
Easier to handle than smaller in-the-canal models.
-
Suitable for individuals with dexterity issues.
-
Can accommodate various advanced features, such as volume control and telecoil.
Disadvantages:
-
More visible compared to in-the-canal models.
-
Susceptible to earwax buildup.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with mild to severe hearing loss.
-
Those who prefer an easier-to-handle hearing aid.
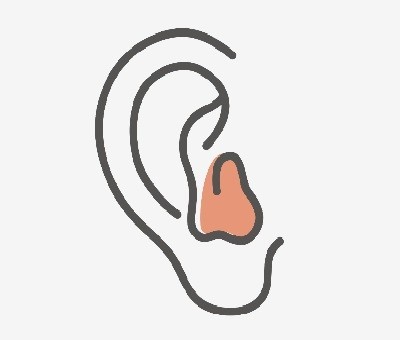
4. In-the-Canal (ITC) Hearing Aids
Description:
ITC hearing aids are custom-molded to fit partially inside the ear canal, making them smaller and less noticeable than ITE models.
Advantages:
-
More discreet than ITE hearing aids.
-
Provides natural sound quality.
-
Offers some advanced features while maintaining a smaller size.
Disadvantages:
-
Smaller controls may be challenging for individuals with dexterity issues.
-
Shorter battery life compared to larger models.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with mild to moderately severe hearing loss.
-
Those seeking a balance between discretion and functionality.
5. Completely-in-Canal (CIC) Hearing Aids
Description:
CIC hearing aids are custom-made to fit entirely within the ear canal, making them nearly invisible.
Advantages:
-
Extremely discreet and cosmetically appealing.
-
Provides a more natural sound experience by utilizing the ear’s natural acoustics.
Disadvantages:
-
Smaller size makes them more difficult to handle and adjust.
-
Shorter battery life due to compact design.
-
Limited space for advanced features.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
-
Those prioritizing discretion and a natural listening experience.
6. Invisible-in-Canal (IIC) Hearing Aids
Description:
IIC hearing aids are the smallest type, inserted deeply into the ear canal, making them almost completely invisible.
Advantages:
-
Nearly undetectable.
-
Provides natural sound localization.
Disadvantages:
-
Requires professional fitting and removal.
-
Not suitable for individuals with severe hearing loss or smaller ear canals.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with mild to moderate hearing loss.
-
Those who prioritize maximum discretion.
7. Bone Conduction Hearing Aids
Description:
Bone conduction hearing aids work by transmitting sound vibrations through the bones of the skull directly to the inner ear, bypassing the outer and middle ear.
Advantages:
-
Beneficial for individuals with conductive hearing loss or single-sided deafness.
-
Does not block the ear canal, allowing for natural airflow and comfort.
Disadvantages:
-
Requires a specific type of hearing loss to be effective.
-
Typically larger and more noticeable than traditional hearing aids.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with conductive hearing loss or single-sided deafness.
-
Those unable to wear traditional hearing aids due to ear canal issues.
8. CROS & BiCROS Hearing Aids
Description:
-
CROS (Contralateral Routing of Signal): Designed for individuals with hearing loss in one ear while the other ear has normal hearing. It transmits sound from the impaired ear to the functioning ear.
-
BiCROS (Bilateral Contralateral Routing of Signal): Designed for individuals with hearing loss in one ear and some degree of hearing loss in the better ear.
Advantages:
-
Improves speech understanding and sound awareness for those with single-sided deafness.
-
Helps users experience a more balanced hearing perception.
Disadvantages:
-
Requires adaptation and time to adjust to the sound routing.
Who Is It For?
-
Individuals with unilateral hearing loss.
-
Those who struggle with directional hearing.
Conclusion
Choosing the right hearing aid is a critical step toward improving hearing and overall quality of life. Each type of hearing aid offers unique benefits, and selecting the best option depends on your specific hearing loss, lifestyle, and comfort preferences. Consulting with a qualified audiologist is essential to ensure the right fit and optimal performance.
Disclaimer: The information in this guide is for educational purposes only and does not substitute professional medical advice. Always consult a certified audiologist for personalized recommendations.